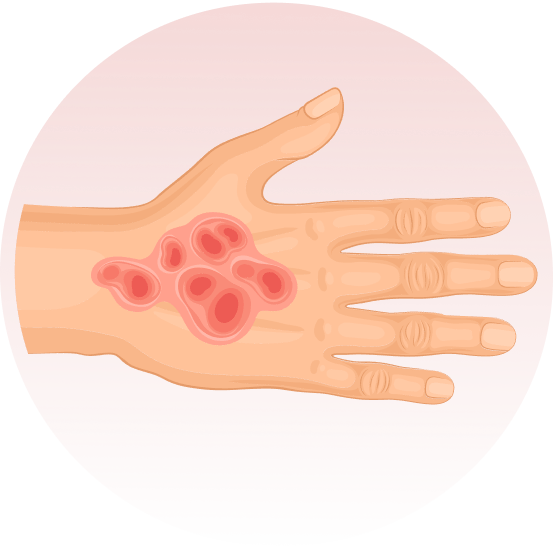
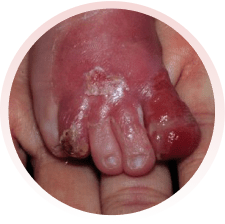
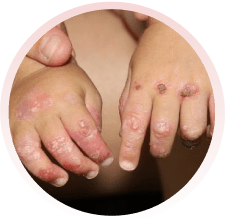
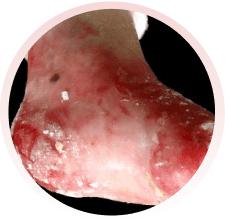
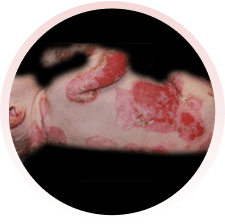
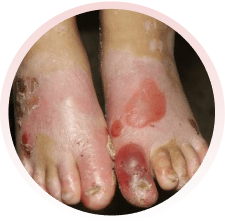
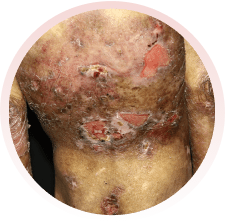
É um grupo de doenças raras, em que surgem bolhas na pele, por qualquer trauma (queda, pelo ato de se coçar, se arranhar, pelo uso de roupas e sapatos apertados ou que machuquem). Elas podem surgir logo ao nascimento ou nos primeiros anos de vida. Não são doenças contagiosas e geralmente são transmitidas de pais para filhos.
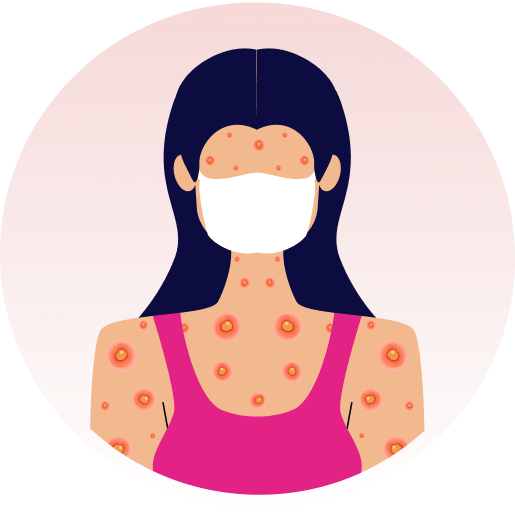

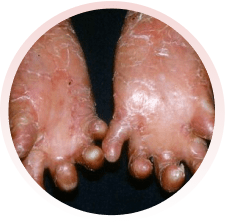
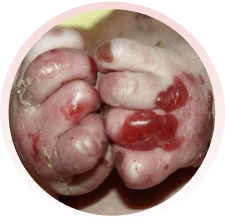
Há vários tipos da doença, alguns com formação de maior número de bolhas e outros com menos bolhas. Alguns tipos podem afetar também a boca, os olhos, o esôfago, os dentes, as unhas, os cabelos e as articulações. Algumas formas da epidermólise podem evoluir com os dedinhos grudados, anemia, desnutrição e infecção das feridas.
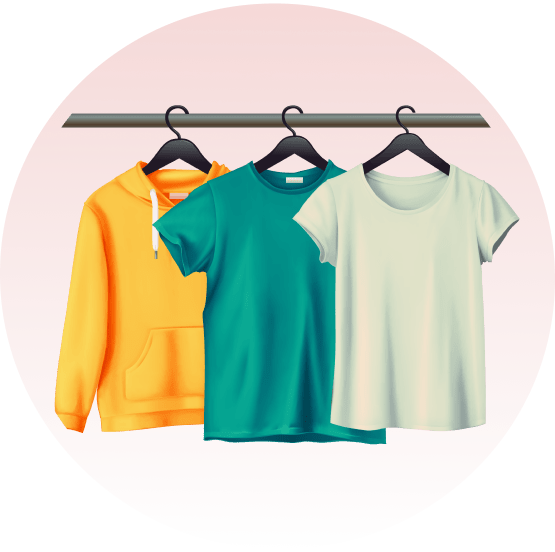


Devem ser orientados por médicos e profissionais especializados da área da saúde. Recomenda-se utilizar roupas e sapatos largos e macios, sem costuras internas e que não machuquem. Evitar alimentos de consistência endurecida, que possam machucar ao engolir. O banho deve ser diário e, se necessário, podem ser utilizadas medicações para dor. Recomendam-se curativos frequentes nas feridas, com materiais não aderentes (que não grudem), inclusive para os dedos.
A criança deve ser estimulada a conviver com outras crianças e adultos, a frequentar a escola, a brincar de maneira cuidadosa. Como a doença não é contagiosa, não há restrições quanto a frequentar lugares públicos.

Contamos com a sua ajuda.

Tel: +55 (11) 98927-3410